Damage to the articular cartilage
Hip arthroscopy can play an important role in the diagnosis of articular cartilage damage, as early lesions (separation, delamination, chondral free flaps) cannot be detected with the conventional diagnostic tests but only by classic MRI or MR arthrography, reaching a sensitivity and a specificity of 90% and 91% respectively.
Instead, the arthroscopic technique sensitivity and specificity is as high as 100%. Furthermore, therapeutic techniques for chondral lesions can be used: sealing / smoothing with radiofrequency device or arthroscopic shaver, the removal of the flaps, the microfracture technique by which fibrous cartilage is formed, or gluing technique of the detached flaps with special fibrin glue. The efficacy of these techniques depends on the extend of the lesions and how early these were diagnosed.
Microfracture technique of cartilage defects in the acetabulum
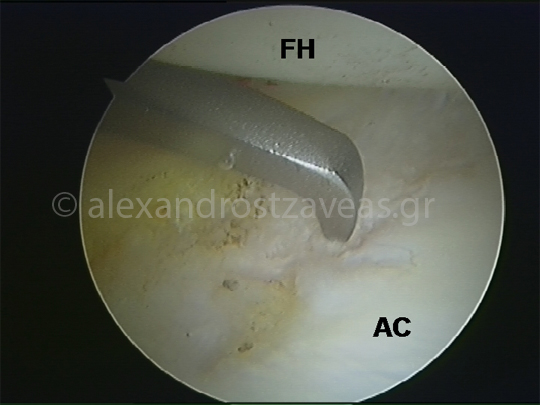
Microfracture technique in cartilage defects of the acetabulum. (FH: femoral head, AC: acetabular articular cartilage)
Technique using fibrin
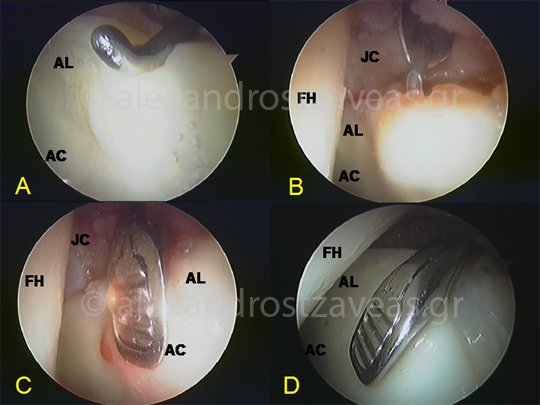
Fibrin glue technique. (A: Assessment of damage - "wave sign", B: injection of fibrin through needle C: fixation with arthroscopic cartilage flap forceps, D: the image after coagulation of fibrin (FH: femoral head, AL : labrum, AC: acetabular articular cartilage, JC: joint capsule)








